Today’s competitive data-driven market demands good quality data for global B2B marketing. Poor data refers to data that is inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated. The cost of bad data is high for organizations, as it prevents them from making informed decisions.
According to a report by Gartner, poor data can cause an average loss of $15 million per year. Moreover, it costs B2B marketers around 10% of their ROI. Hence, it is crucial to practice caution against bad data quality.
In this blog, we will explore what bad data is, the cost of bad data, and how to improve data quality to maximize returns.
What is Bad Data Quality
Any incorrect information, such as an old email address or a non-functional phone number, can be referred to as bad data.
In the current business scenario, with a majority of marketing initiatives depending on authentic B2B data, the cost of bad data quality is at an unfortunate high. The main reasons behind bad data quality are poor interpretation, human error, technology issues, or data collected from erroneous sources.
A minor discrepancy in the contact number or a misspelt name can be counted as misinformation which can cause potential critical losses for an organization. It also impacts customer trust and regulatory compliance.
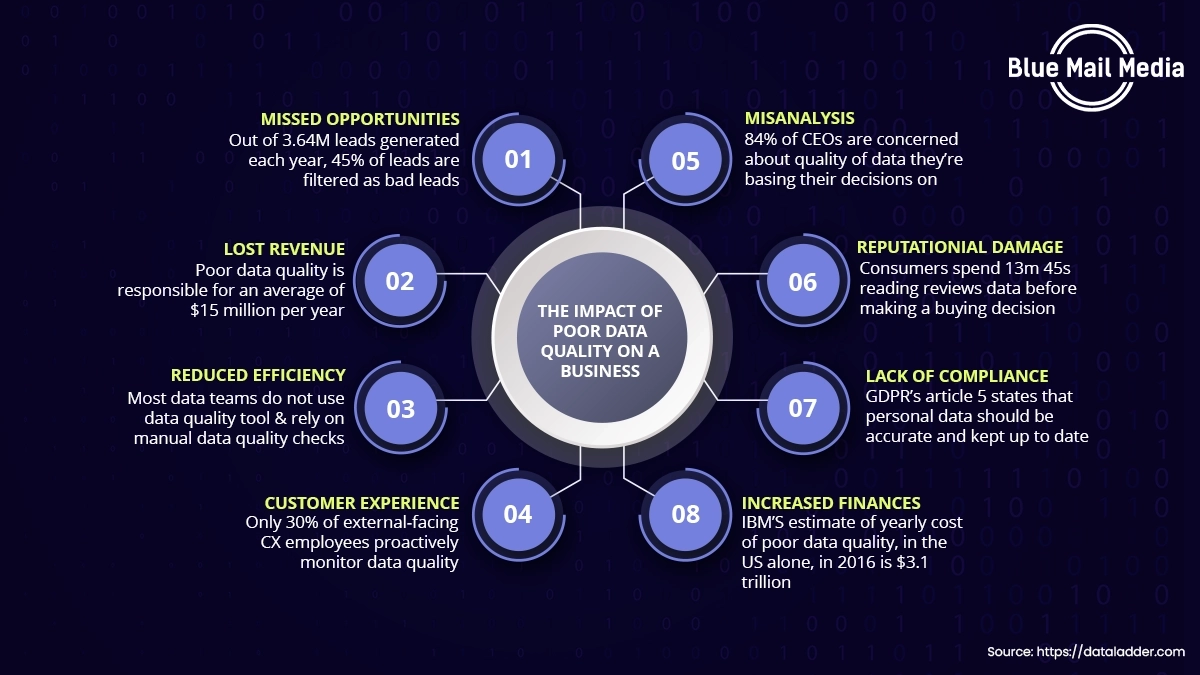
The Cost of Bad Data Quality
Bad data quality can lead businesses to incur major financial losses and cause significant setbacks in their marketing objectives. Therefore, it is essential to be mindful of the cost of bad data and collate data from reliable and legal sources.
Here is a list of the cost of bad data quality that negatively impacts an organization:
1. Financial Losses
Inaccurate data in the B2B marketing sector can cause significant discrepancies in financial analysis, planning, and forecasting. Poor data can result in wrong financial reports that lead to bad investments.
2. Dissatisfied Clients
The cost of poor data quality also includes major setbacks in customer retention and brand loyalty. Poor data facilitates misinformation, which causes customer service representatives to provide inaccurate assistance. This can result in unsatisfied customers, reduced lead conversions, and negative financial implications for the business.
3. Reduced Efficiency of Sales and Marketing Initiatives
Marketing campaigns can fail if target audiences are incorrectly identified. Businesses may also have trouble reaching their ideal clients if their customer segmentation is poor, which can negatively impact their sales growth.
4. Inefficiency in Workers Leading to Higher Operational Costs
A brand’s hindered reputation and lack of business conversions are only two significant costs of incorrect data. B2B marketers also have to incur the cost of poor data with the inefficiency of their staff.
Employees may lose time working with inaccurate data or trying to amend obsolete data with little attention to detail.
This inefficient working process can discourage data scientists, as a majority of time and effort is wasted.
On average, data scientists spend 60% of their time polishing data. The manual correction of inaccurate data causes organizations to incur significant losses. Therefore, the additional labor and software investments needed for data cleansing, duplication, and rectification can increase the overall operating costs.
5. Inefficiencies in Operations
Poor data quality can delay work progress and hinder efficient operations systems. For instance, inaccurate inventory data may result in stock outs or overstocking, which can interfere with supply chain management.
6. Compliance Violations and Penalties
Breaking data protection laws like the GDPR or HIPAA can lead to harsh fines. Moreover, inadequate handling of consumer data can harm the company’s reputation.
Data breaches and issues with data integrity are among the many costs of bad data quality. It may result in legal and financial repercussions.
7. Missed Business Opportunities
Poor data quality may result in missed opportunities, such as failing to recognize new industry trends or possible collaborations. Around 57% of businesses learn about their data discrepancies only when it gets reported by prospects. These missed opportunities may affect the development of the businesses.
8. Inaccurate Business Analytics
Data-driven insights are essential for strategic decision-making. One significant cost of bad data quality is biased analytical results, leading to erroneous conclusions. This makes it difficult for businesses to take advantage of their growth prospects.
9. Losing the Competitive Edge
Businesses that rely on data for a competitive edge may be outperformed by rivals that have access to higher-quality data. Inaccurate marketing knowledge and customer insights could lead to poor brand positioning.
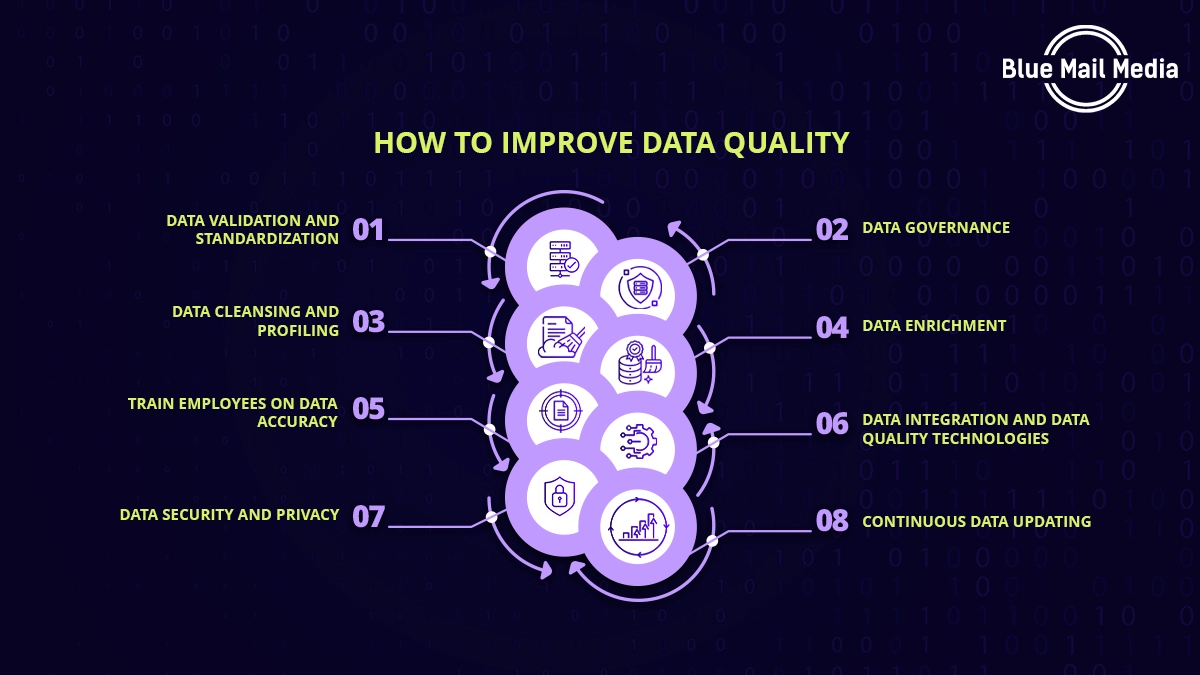
How to Improve Data Quality
The quality of data determines an organization’s overall trajectory of business productivity. Hence, correcting data discrepancies is crucial for improved B2B marketing and achieving long-term business goals.
Therefore, data quality must be improved so enterprises can make informed decisions. Here are some methods to improve data quality and avoid the cost of bad data:
1. Data Validation and Standardization
- Businesses can use automatic data validation tests during data entry to ensure data accuracy and relevance.
- Standardize data values and formats to preserve uniformity throughout the database.
- Use dropdown menus and prepared lists to reduce manual data entry errors.
2. Data Governance
- Establish a solid data governance architecture with distinct roles, responsibilities, and data ownership.
- Create and enforce data quality standards throughout the organization.
- Conduct periodic checking of data quality to ensure the implementation of policies and procedures for clean data entry.
3. Data Cleansing and Profiling
- Check data quality metrics, such as KPIs, to measure and track the performance of campaigns regularly.
- Keep track of data quality and address potential issues to prevent the cost of bad data quality.
- Use automated data cleansing software to save time and money.
4. Data Enrichment
- Enhance and update data with relevant information from reputable and legal sources such as surveys, questionnaires, newsletters, office directories, periodicals etc.
- Clean and enriched data will provide clarity and help in informed decision-making for the business.
5. Train Employees on Data Accuracy
- Train employees to be responsible and handle data better to avoid the cost of bad data quality.
- Educating them about the role they play in maintaining data quality can ensure the elimination of inaccurate data.
6. Master Data Management
- Use Master Data Management or MDM tools to keep a single, trustworthy source of information for important data.
- MDMs can ensure data consistency across various platforms.
7. Set Similar Values of Common Data
- Data errors can be made when users enter freeform or unstructured data. It can lead to spelling, input, or abbreviations errors.
- For example, a common data field, such as the name of the State Pennsylvania could be typed as Penn or misspelt as ‘Pensylvania’. Users should be mindful of the names of common data fields to avoid inconsistencies.
- Therefore, create a limit for unstructured data and allot common values to particular data entry fields.
8. Data Integration and Data Quality Technologies
- Use technologies for data quality that can detect and correct problems to ensure high-quality data.
- Utilize data integration technologies to combine data from diverse sources effortlessly.
- The quality checks can be performed as a combined process with automatic and manual checks.
9. Data Security and Privacy
- Implement strict data security measures to shield sensitive data from breaches and unauthorized access.
- Comply with privacy laws to preserve data integrity and retain customer loyalty.
10. Designate a Data Steward
- The data steward will act as the authorized personnel to ensure the accuracy and relevancy of the data.
- They can act as a data monitor and address data quality issues.
11. Continuous Data Updating
- Ask for regular inputs from the data consumers to spot relevant issues with data quality.
- Constantly enhance data quality procedures through regular updates in response to customer input and altering business requirements.
Final Words
Organizations must establish a trustworthy data environment to avoid the high cost of bad data, as it consumes significant time, and financial investments. Companies can collaborate with a reputable B2B data solution provider like Blue Mail Media for effective B2B marketing solutions.
Blue Mail Media team has a comprehensive understanding of data administration and analysis and can add a level of expertise and experience that might not be easily accessible internally.
Go through their case studies to learn about the improved data quality and effective B2B data solutions that significantly increase revenue for your organization.